TDS Online Payment
TDS or Tax Deducted at Source is a mechanism through which one pays tax in India as per the provision of the Income Tax Act, of 1961. The deductor whether it is a person, institution, or organization, is required to withhold an amount equal to the tax amount from the total earnings payable to the receiver or deductee.
It is the job role of the deductor to ensure that tax deductions should be done correctly. It is deposited with the concerned authorities within a stipulated timeline.
Applicability of TDS in various forms:
- Income from interest on securities and debentures.
- Income from interest other than those on securities.
- Income from dividends.
- Income from the withdrawal of EPF (Before the expiry of a certain period or if the amount withdrawn is beyond the limit specified).
- Payment to contractors/subcontractors/freelancers.
- Winnings from horse races, lottery, crossword puzzles, or any game-related wins.
- Insurance commission and commission on brokerage earnings
- Transfer of certain immovable property, etc.
- Income from rendering technical or professional services
- Income from royalty, etc.
Reason for introducing TDS
- To prevent tax evasion: This mechanism ensures that the government is collecting a part of the total payable tax at the time of receiving the Income Tax itself. It helps in minimizing the chances of tax evasion.
- It acts as a source of steady revenue for the government throughout the year.
- Timely collection of tax.
- Convenience for taxpayers: This mechanism ensures that the government is collecting a part of the total payable tax at the time of receiving the Income Tax itself. It helps in minimizing the chances of tax evasion.
- Ease in filing tax returns: As tax collection is done automatically and deposited within the concerned authorities by the deductor, it becomes easier for individuals to file their Income Tax Returns. In case the person has no other source of income and TDS has been appropriately deducted, there is no need to pay any other tax at the time of filing the Income Tax Return.
Importance of TAN or TDS
- TAN or Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number is a 10-digit alphanumeric number issued to organizations or individuals that are required for making deductions and collections of tax on payments made by them.
- As per the provision of Section 203A of the Income Tax Act 1961, it is mandatory for all people or organizations who are liable for deducting tax of employees to quote TAN details in matters and correspondences related to TDS such as TDS returns, TDS Payments, issuance of Form 16, etc. with Income Tax Department. If anyone fails to follow the norms, then there is a penalty of Rs 10,000 on the organization or institution that is liable to deduct tax.
- If anyone fails to follow the norms, then there is a penalty of ₹ 10,000 on the organization or institution that is liable to deduct tax.
- Banks do not accept TDS returns and payments unless the deductor or depositor has a valid TAN.
- Many times, assumptions are made by people that PAN and TAN are one of the same documents. People must know that PAN and TAN are not the same, TAN is to be obtained separately by the organizations and institutions to deduct tax, even if they are having PAN.
- The only exception is in the case of a buyer of an immovable property. In this case, the buyer or the deductor is not required to obtain a TAN and can use PAN for remitting the TDS.
Procedure to apply TAN Application
It is the very easy online procedure for filing up TAN Form 49B
Time of tax Deduction: As per Section 192, Tax on salary is deducted at the time of actual payment and not at the time of salary accrued.
- If in case it is an advance salary or arrears given to an employee, then TDS is to be deducted at the same time.
- All payments that one received from other sources, in these cases, TDS either collected at the time of payment or at the time income is being credited, whichever takes place earlier.
Online TDS Payment
- Online TDS Payment System works on the philosophy of “Anytime, Anywhere”.
- Online TDS Payment streamlined the TDS administration into a user-friendly and transparent process. It also helps in reducing tax fraud cases.
- It is one of the common platforms where taxpayers, deductors, and assessing officers have access to the same data.
- With an increasing number of taxpayers in the country, digitization works as the most essential pre-requisites for making the TDS Payment system accurate, speedy, and stable.
Process of Making an Online TDS Payment
Since January 1, 2014, it is mandated for all other assessee and government deductors who are subjected to compulsory audit under Section 44AB. They are making use of the electronic transfer to make use of the TDS Payment. For availing of the benefits of online TDS payment, the taxpayer is required to have a net-banking account with an authorized bank. The list is available on the NSDL-TIN Website. Online TDS Payment or re-payment is a user-friendly and simple process. It can be done by following the below-mentioned steps.
- Log in to the website of the E-Payment of Income Tax Department - https://incometaxindia.gov.in/Pages/tax-services/pay-tax-online.aspx
- Select the Challan No. ITNS 281 is used for making deposits of TDS/TCS either by a non-company deductee or a company.
- Select the category of the deductee.
- If the deductee is a person then select (0021), Non-Company Deductee, else you need to select (0020) for Non-Company Deductee.
- Fill in the TAN detail for the online verification of the TAN validity.
- If TAN details are not available in the Income Tax Authority’s database, you will not be allowed to proceed further with the process of TDS payment.
- Choose the assessment year and it should be immediately following the financial year in which the income is evaluated.
- Provide the challan details which include the accounting head under which one needs to make the payment. Along with challan details, the name, email address, and contact details of the TAN holder also need to be furnished.
- Select the payment type. If it is a ‘ normal payment’ then select (200) TDS/ TCS Payable by the taxpayer and if a payment is against the demand raised by the Income Tax Department such as making an interest payment or late fee under section 234E then select (400) TDS/TCS regular assessment ( raised by the Income Tax Department).
- Select the nature of payment such as payment of insurance commission, fees for professional services, rent, etc.
- Choose the bank through which you want to make the TDS payment.
- After the submission of the required details, the confirmation screen would get displayed.
- Check the details thoroughly as you need to confirm that all the data which is mentioned in the challan is correct and true to the best of your knowledge.
- Post the confirmation, you will be redirected to the net-banking page of your bank. Log in to the same by making use of your User ID and password.
- After making an online TDS Payment successfully, the system generates a challan Counterfoil.
- Challan details include – the Challan Identification number which shows the bank name, payment details, Bank Branch Code, and date of tender in the context of e-Payment made.
- The collecting bank branch transmits the details of taxes deposited to the “Tax Information Network’’ through the online Tax Accounting system.
- You can also verify the status of Challan in the ‘’Challan Status Inquiry’’ on the NSDL- TIN Website post 7days of making an online TDS Payment.
- If facing any issues at the website of NSDL, a taxpayer can contact TIN customer care at 020 – 27218080 or write to them at tininfo@nsdl.co.in.
TDS Certificate
TDS certificate, Form16, and Form 16 A issued on an annual or quarterly basis. After making a TDS payment with the Income Tax Department, as per the provision of Section 203, the deductor is required to provide a TDS certificate to the person on behalf of whom the tax payment was being made.
Benefits of making online TDS Payment
- One can make a payment of TDS anytime as the payment gateway remains open 24x7x365.
- Deductor also makes the TDS payment on behalf of the deductee as per convenience in terms of time and location.
- Immediate acknowledgment of the payment. One can download a copy of the acknowledgment and save it for future reference.
- Reduced charges of corruption and malpractices such as discretionary grant credit of tax deductions based on manual TDS Certificates.
- Less paper translates into being environmentally friendly.
Timelines for making TDS Payment
- The due date for TDS payment collection by the deductor sets as the 7th of the next month. For example, the deductor needs to pay TDS for the month of ‘June’, on or before 7th July.
- Only for the ‘March’ month, considering as the end of the Financial year, the deductor can pay TDS deducted on or before 30th April of that year.
- These timelines are applicable for all the deductors be it is non-government assesses or a Government assesses whosoever makes deposit tax along with the Challan.
- For government deductors who make the TDS payment without challan, the due date for payment of TDS is the same day on which the tax amount is deducted.
- In some scenarios, the Assessing officer with pre-approval from Joint Commissioner allows quarterly payment of TDS. In case the last date of payment is the 7th of the next month after the end of each quarter and the 30th of April for the last quarter of the financial year.
What is E-TDS Return?
Since June 1, 2003, all corporate deductors are required to submit TDS returns in an electronic form which is known as E-TDS Return.
From Financial Year, 2004-2005 onwards, furnishing e-TDS returns is also mandatory for government deductors.
Deductors (other than government and corporates) may file TDS returns in electronic or physical form.
Important factors related to TDS Returns
- Central Board of Direct Taxes has authorized NSDL e-Governance Infrastructure Limited, (NSDL e- Gov), Mumbai, as an e-TDS intermediary.
NSDL e-Governance has established TIN Facilitation Centers (TIN-FCs) across the nation for facilitating collectors or deductors to file their e-TDS returns. - Whether you will form online or offline, filing the TDS returns are the same.
- E-TDS statements should be prepared as per the file format (clean text ASCII File) following the specifications provided by the Department of Income Tax.
- To have ease of E-TDS statement preparation, the government comes up with a free and downloadable software (Return Preparation Utility- RPU) that has been developed by NSDL.
- There are also many third-party software vendors to whom the task of preparing e-TDS Statements can be outsourced.
- One can check the list of approved vendors that are available on the NSDL -TIN website (www.tin-nsdl.com).
What happens if one misses the above deadlines?
Case I – Delay in TDS deduction
TDS Deduction needs to be done by the 30th of each month and in February, the deduction should take place by the last day of the month.
If TDS is not deducted on or before the due date, whether in whole or in part, then the concerned deductor becomes liable to pay interest. It is applicable at the rate of 1% per month or part thereof from the date when it should have been deducted to the actual date of deduction.
For instance, if the TDS Amount was to be deducted for July (i.e. 30th of July), but it was collected on the 5th of August, then interest will be 2% (For July and August).
Case II – Delay in TDS Payment
- If the TDS which is deducted is not deposited with concerned authorities within a stipulated time period, whether in whole or in part according to Section 201(1A), the deductor becomes liable to pay an interest, which is applicable at a rate of 5% for every month or part thereof, from the date TDS was collected to the date on which such tax was actually remitted to the credit of the Government.
- A calendar month is considered to calculate the interest and any fraction of a month is deemed to be a full month.
- Even a delay of one day would mean that you need to pay interest for two months.
- In case TDS is deducted in July and deposited on the 8th of August then you must pay interest for 2 months i.e. July and August. The total interest payable shall be 3%.
Additional provisions for penalty and prosecution proceedings as well :
Penalty under Section 221
- In case the Assessing Officer is convinced that the assessee has failed to make tax deductions as per requirement without any valid reason, the defaulter is liable to imposition of penalty.
- The quantum of the penalty cannot be more than the amount of tax in arrears.
Penalty under Section 271C
A penalty equal to the amount of tax that the deductor has failed to deduct can be imposed. However, such a penalty can be levied only by a Joint Commissioner of Income Tax.
Prosecution proceedings under Section 276 B
Where the deductor fails to make a deposit of Tax deducted at source, with the concerned government authorities, without a reasonable cause, he/she is liable to be punished with rigorous imprisonment for not less than 3 months to 7 years and with a fine.
Case III - Delay in TDS Return Filing
- According to Section 234E, in case the assessee fails to make a submission of the TDS return on or before the specified due date, a penalty of Rs 200 on a per-day basis would be imposed till time TDS return is submitted.
- The penalty amount should not exceed the total amount of TDS Collection.
- This penalty is applicable at the time of furnishing Form 26 QB, in case of purchase of immovable property.
Delay in filing of TDS returns for more than a year from the due date or submission with inaccurate data such as TAN, Challan Number, TDS Amount, etc. will attract a minimum penalty of ₹ 10,000 and not be more than ₹ 1,00,000.
The process to check TDS Payment status
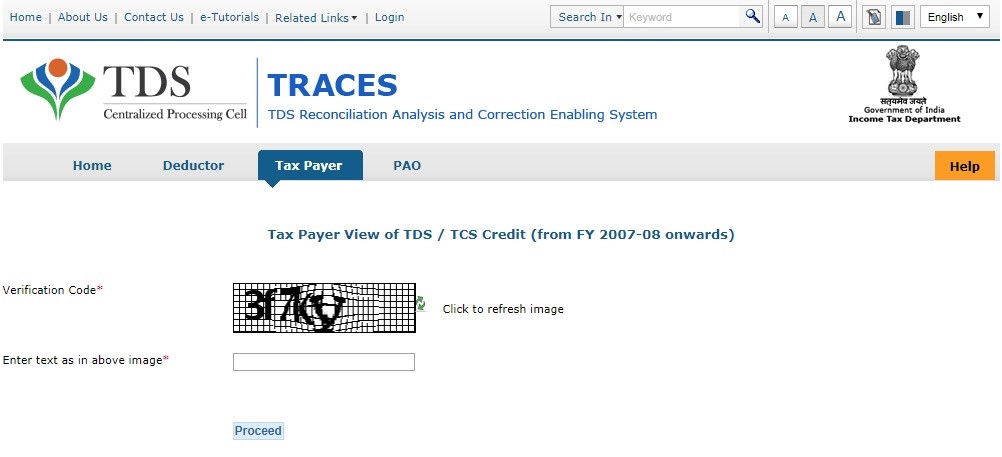
The steps to follow are:
- Log in to the website of https://www.tdscpc.gov.in/app/tapn/tdstcscredit.xhtml.
- Enter the captcha code and click on “Proceed”
- Fill in the details required such as TAN of the deductor, PAN of the deductee, Financial Year, Quarter, and Type of Return. Click on “Go” now the TDS credit of the taxpayer is displayed on the screen.
TDS Due dates
| Deduction Month | Quarter end date | TDS Payment Due Date | The due date for filing returns |
| April | 30th June | 7th May | 31st July |
| May | 30th June | 7th June | 31st July
|
| June | 30th June | 7th July | 31st July
|
| July | 30th September | 7th August | 31st October
|
| August | 30th September | 7th September | 31st October
|
| September | 30th September | 7th October | 31st October
|
| October | 31st December | 7th November | 31st January
|
| November | 31st December
| 7th December | 31st January
|
| December | 31st December
| 7th January | 31st January
|
| January | 31st March | 7th February | 31st May
|
| February | 31st March
| 7th March | 31st May
|
| March | 31st March
| 7th April | 31st May
|
